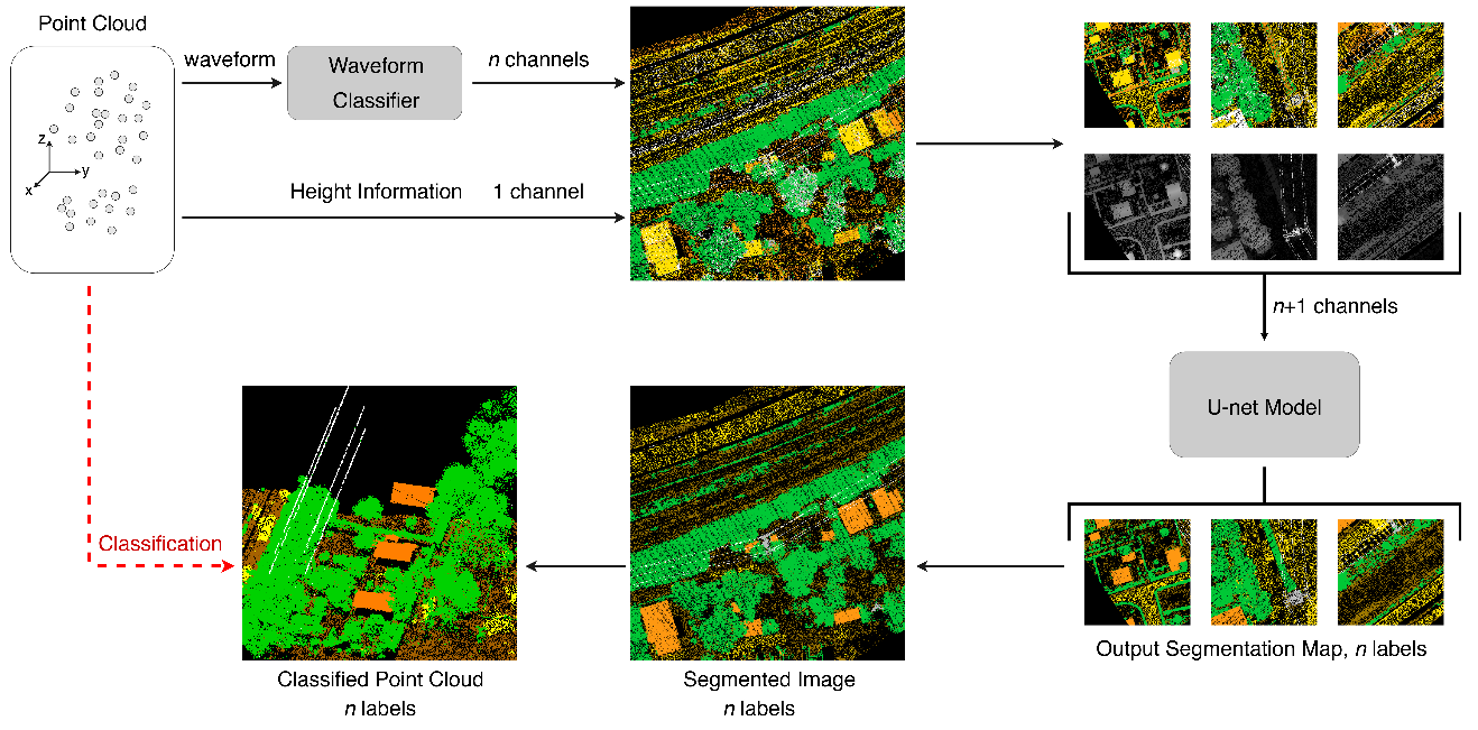
LiDAR technology is widely used in remote sensing, as it allows to obtain a 3D model of the surveyed environment in the form of a point cloud, measuring the time taken by a short laser pulse to travel the distance between the instrument and the object to be measured.
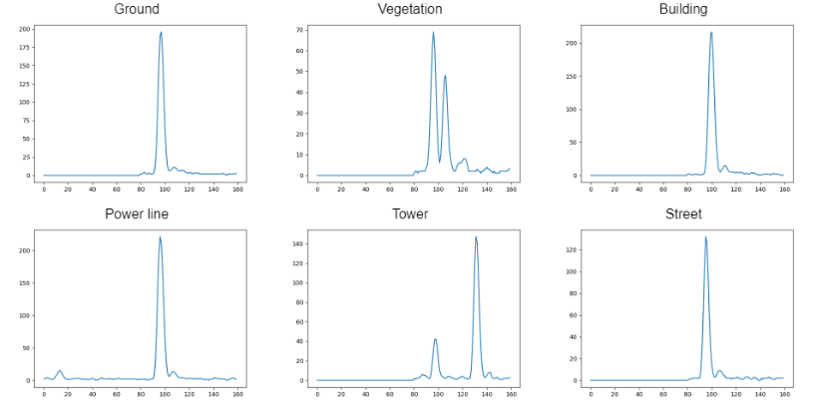
Among the different types of LiDAR sensors, the full-waveform laser scanner is able to record as a function of time the entire distribution of reflected energy from the surfaces hit by the laser pulse (waveform). Thanks to this data it is possible to obtain further information on the geometric and reflectivity properties of the target, useful in the classification phase. Classifying the laser data means assigning to each detected point its class, according to the object hit by the laser pulse.
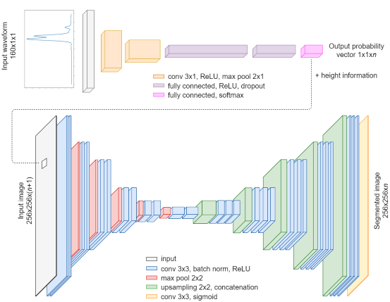
The patented solution aims to classify the data in two stages: in the first one, the raw waveform data is provided as input for a classifier. In the second step, the data is mapped into a two-dimensional image, in which each pixel contains the probability distribution vector provided by the classifier, and the height of the point falling into the pixel. A deep learning algorithm is then used to segment the image, assigning a label to each pixel. The method thus allows a fully automatic classification that, compared to current technologies, improves the achievable accuracy.