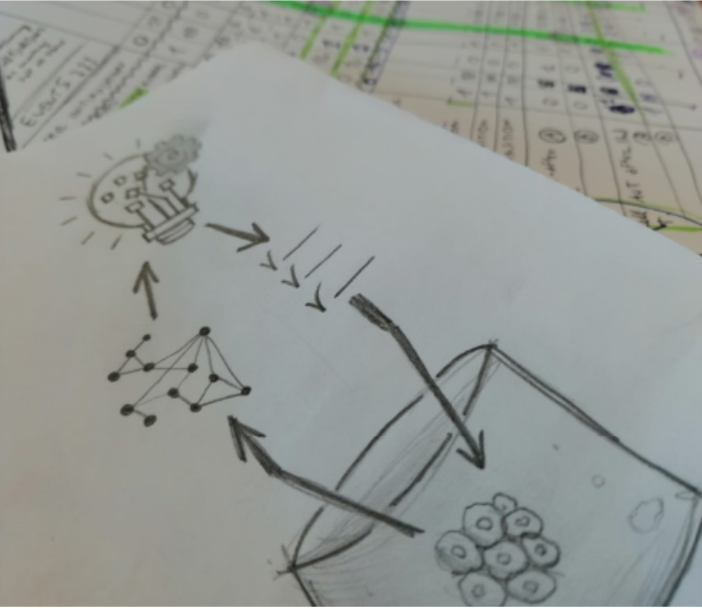
Digitization and automation are employed to make the overall R&D process more traceable, reproducible and efficient. The optimization of culture protocols follows Design of Experiment (DoE) paradigms, aiming to make existing protocols more effective, focusing on functional aspects only, and not on the processes that present structural complexities as well, such as the biofabrication of tissues and organs for regenerative medicine. Structural aspects are dealt with in the design of structures for bioprinting, which do not deal with biological and functional aspects though.
Cultūrā is different from competitors for the type of impact it has on the biofabrication process, and for the degree of structural complexity of the products it targets. Mogrify computationally generates groups of factors for cell differentiation, but considering only functional aspects, while our solution also considers structural aspects, and manages the different phases of differentiation.
Ginko Bioworks modifies microorganisms to improve industrial biotechnological processes. It aims to improve the R&D process yet using a different strategy, based on genetic engineering.
Other computational approaches are solutions adjacent and potentially synergistic with ours, for example Synthace, partner of Microsoft Station B, a platform to digitize the entire experimental laboratory process, RoosterBio and Riffyne Orgenesis, which are automation services, relying on digitization and process design.