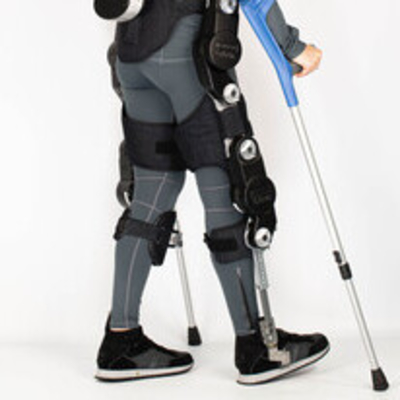
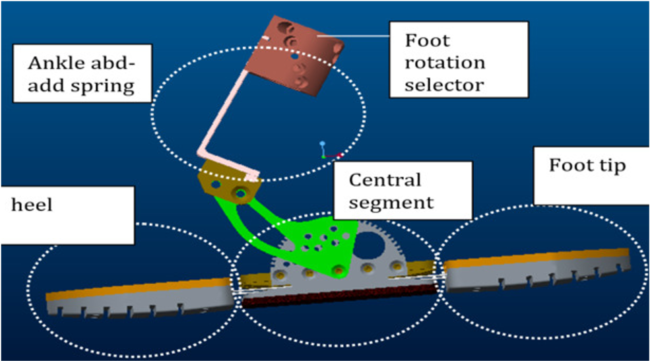
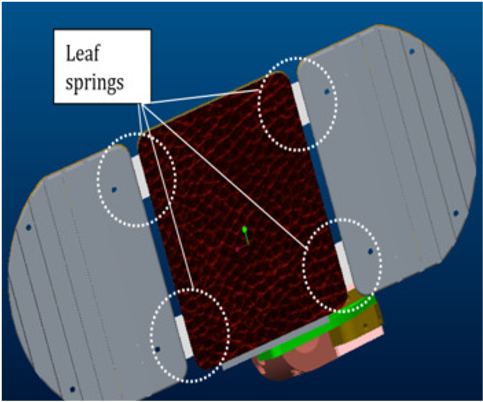
The footsole presented here exploit its flexibility to replicate a more human-like gait. It is made of three rigid segments (heel, center, tip) connected through armonic steel – made leaf springs. The springs are constrained to deflect on a curved surface such that the active length of the spring shortens for a growing deflection angle between the central segment and the heel or the tip thanks to an appropriate profile of the housing. This allows for a stiffening of the two joints for growing deflection to avoid the joint to reach the end-stop during normal walking conditions. Strain gauges are glued onto the leaf springs to measure the force/torque exerted on the foot and estimate the deflection angle. The ankle flexion/extension is implemented through another leaf spring. The sole uses a ”zero” angle selector that is used to set the no load ankle flexion/extension position of the footsole.