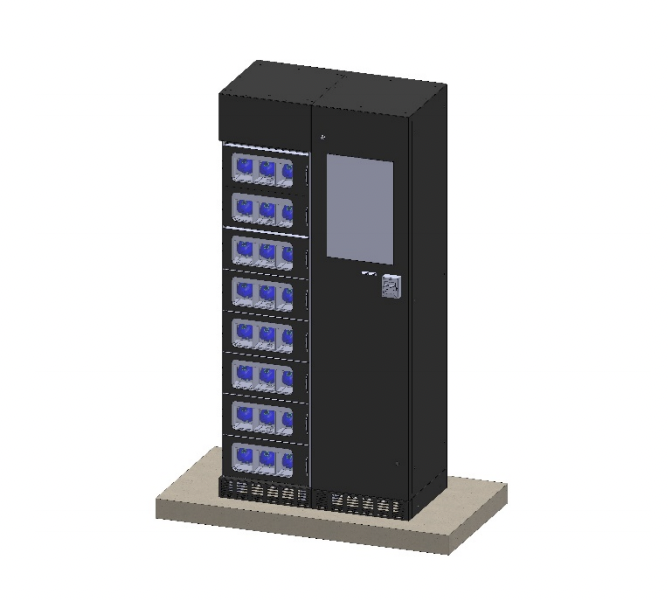
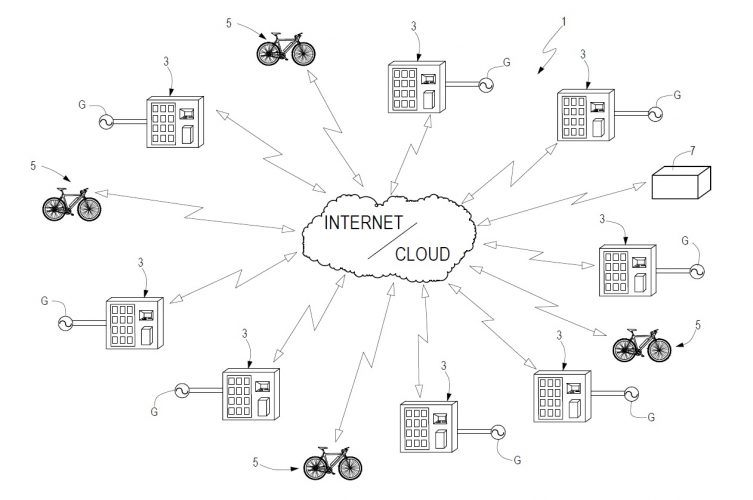
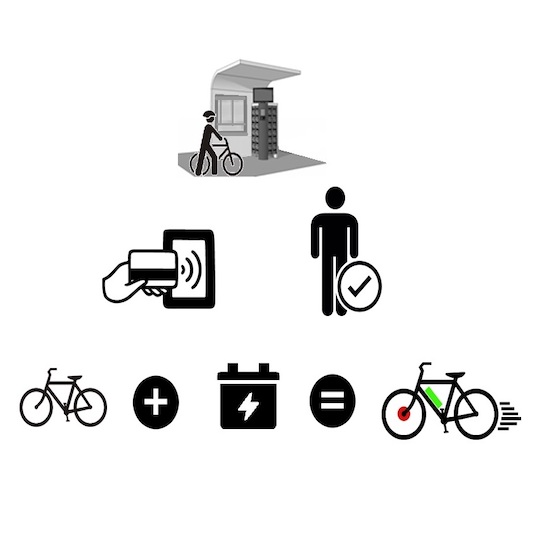
The invention consists of a system for sharing rechargeable battery packs made available, for the means of transport of the users of the system itself, in appropriate charging stations distributed throughout the city. The monitoring and management of the service takes place through the exchange of data between the charging stations, the battery packs and a central control unit. The patent provides that packs of rechargeable batteries for soft mobility are integrated into appropriate recharging stations which, in addition to performing the function of recharging the individual packs, allow them to be shared among the users of the service. The user, enabled to access the service, can rent the battery pack to power his vehicle, for example a pedal assisted bicycle, and only bear the cost of recharging the battery. The patented system also provides a control unit for the management and monitoring of the service. The control unit, continuously connected to the charging stations and battery packs, will also allow users and the operator to be provided with the respective information of interest, such as the use of the battery packs, their state of charge and life. useful, their geo-localization, environmental monitoring and more.