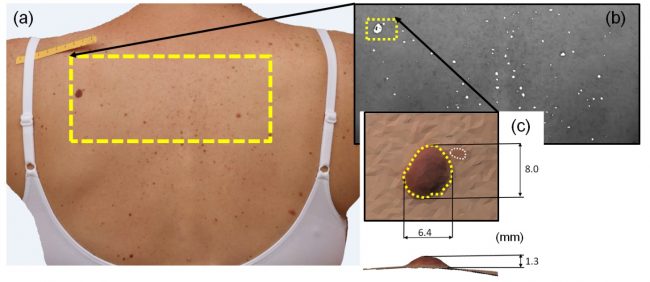
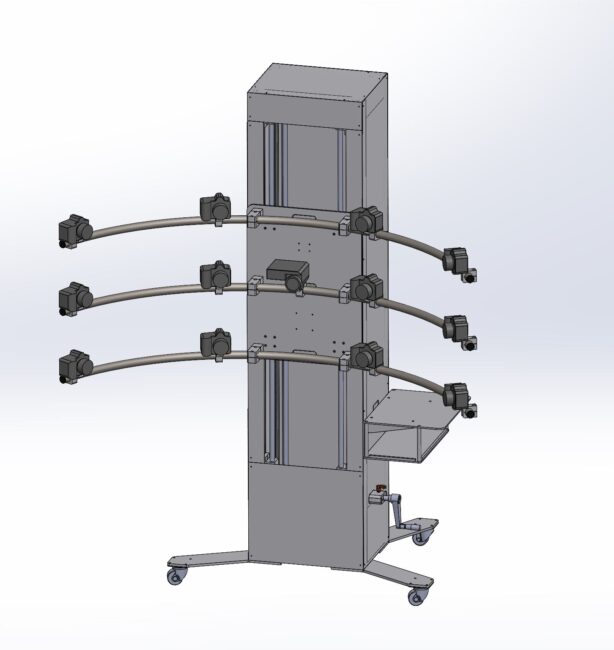
The prototype currently in use for experimental clinical validation at the Istituto Oncologico Veneto Cancer Institute, is able to acquire data related to the skin of the patient’s back, thanks to the data provided by 12 synchronised cameras (operating in polarised light) and a thermal camera, positioned on a curved and mobile frame.
The calculation of the risk factor index associated with each nevus is achieved through the work of convolutional neural networks (CNN) that classify the information acquired during screening on the basis of the information acquired during training and comparison with previous screenings.
The data acquired include:
- Photographic data;
- Photogrammetric modelling, which returns the nevi geometry obtained from polarised light images with 0.2mm resolution;
- Fusion of chromatic and thermal data;
- Correlation of the thermographic data with the level of vascularisation;
- Comparison with screening from previous examinations to detect variations.
The system provides an output in DICOM format:
- The 2D model of the skin with indication of the melanoma risk factor index for each skin lesion detected
- The set of data that characterise the nevi identified as having the highest risk factor.
The DICOM format is universally used for the management of diagnostic imaging data and does not require proprietary software for consultation.
The set of these outputs therefore allows a clear and objective assessment of the evolution of many nevi over time, as well as an evaluation of the risk factor of each mole thanks to the power of artificial intelligence.